Can Oral Thrush Indicate Bacterial Imbalance and Oral Infection Risk
Oral thrush can indicate a bacterial imbalance in your mouth, raising your risk of oral infections. The overgrowth of Candida yeast disrupts the normal microbial balance, allowing harmful bacteria to thrive. This can lead to conditions like periodontitis and increased inflammation. Key risk factors include a weakened immune system, antibiotic use, and poor oral hygiene. Understanding these connections is essential for effective management and prevention of oral thrush and its complications. More insights await you on maintaining oral health.
Key Takeaways
- Oral thrush results from Candida overgrowth, disrupting the normal microbial balance in the mouth.
- This disruption increases the risk of bacterial infections, such as periodontitis.
- Conditions like weakened immunity and antibiotic use can exacerbate this imbalance.
- Symptoms of oral thrush include white patches, soreness, and difficulty swallowing.
- Prompt diagnosis and treatment of oral thrush are essential to prevent further infections.
Understanding Oral Thrush: Causes and Symptoms
Oral thrush, a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida yeast, can lead to discomfort and complications if left untreated. This condition often arises due to microbial dysbiosis, where the natural balance of microorganisms in your mouth is disrupted. Factors such as antibiotic use, a weakened immune system, or poor oral hygiene can contribute to this imbalance, allowing Candida to proliferate. Symptoms of oral thrush include white patches on the tongue and inner cheeks, soreness, and difficulty swallowing. You might also experience a cottony feeling in your mouth. Recognizing these signs early is essential, as untreated oral thrush can lead to more severe infections, making timely intervention vital for maintaining your oral health.
The Role of Candida in Oral Health
Candida plays a complex role in oral health, acting as both a normal inhabitant of the mouth and a potential pathogen. When there’s a bacterial imbalance, Candida can overgrow, leading to oral candidiasis, which increases your infection risk. Here are three key aspects of Candida’s role:
- Normal Flora: Candida is typically present in small amounts, contributing to a balanced oral microbiome.
- Pathogen Potential: An overgrowth can result in oral candidiasis, characterized by white patches and discomfort.
- Immune Response: A healthy immune system usually keeps Candida in check; however, factors like stress or illness can disrupt this balance.
Understanding these roles can help you maintain oral health and prevent complications associated with Candida overgrowth.
What Is Microbial Imbalance?
Microbial imbalance occurs when the natural flora in your mouth gets disrupted, often due to factors like poor diet, medications, or stress. This imbalance can lead to various oral health issues, including an increased risk of infections like oral thrush. Understanding the causes and effects of microbial imbalance is vital for maintaining your overall oral health.
Causes of Microbial Imbalance
An imbalance in the body’s natural flora can lead to various health issues, including oral thrush. This condition often arises when the balance between helpful bacteria and harmful microorganisms, like candida albicans, is disrupted. Several factors can contribute to this microbial imbalance:
- Antibiotic Use: These medications can kill beneficial bacteria, allowing opportunistic pathogens to thrive.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions affecting mucosal immunity can make you more susceptible to infections, like oral thrush.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Neglecting proper dental care can lead to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria and fungi.
Understanding these causes can help you take proactive measures to maintain a healthy oral environment and reduce the risk of infections.
Effects on Oral Health
When your body’s natural balance of microorganisms is disrupted, it can greatly affect your oral health. An imbalance can lead to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria and fungi, such as Candida, resulting in conditions like oral thrush. You may notice symptoms like white patches in your mouth, soreness, and difficulty swallowing. This imbalance can also increase your risk of gum disease and tooth decay, as beneficial bacteria that protect your oral cavity diminish. In addition, the inflammation caused by these infections can contribute to bad breath and discomfort. Maintaining a healthy microbial balance through good oral hygiene, a balanced diet, and regular dental check-ups is essential to prevent these complications and promote overall oral health.
How Oral Thrush Develops in the Mouth
Oral thrush develops when there’s an overgrowth of Candida yeast in your mouth, disrupting the natural balance of microorganisms. Various risk factors, such as a weakened immune system or certain medications, can contribute to this condition. Recognizing the symptoms, like white patches and discomfort, is essential for timely treatment.
Candida Overgrowth Mechanism
Though the mouth hosts a variety of microorganisms, a balance is essential for maintaining oral health. When this balance is disrupted, Candida, a type of yeast, can overgrow, leading to oral thrush. Here’s how this mechanism works:
- Impaired Defense: Your immune system weakens due to stress, medications, or underlying health conditions, allowing Candida to thrive.
- Environmental Changes: Factors like dry mouth or poor oral hygiene create a favorable environment for yeast growth.
- Dietary Influences: High sugar consumption can promote Candida proliferation, as yeast feeds on sugar.
Understanding these mechanisms is vital to preventing oral thrush and maintaining a healthy microbiome in your mouth.
Risk Factors Involved
Several risk factors can contribute to the development of oral thrush, making it important to recognize your vulnerability. Factors like weakened immunity, diabetes, and certain medications can increase your risk. Additionally, poor oral hygiene and wearing dentures can create an environment conducive to Candida overgrowth.
Here’s a table summarizing these risk factors:
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Oral Thrush |
|---|---|---|
| Weakened Immune System | Conditions like HIV/AIDS | Lowers body’s defenses |
| Diabetes | High sugar levels | Fuels fungal growth |
| Antibiotics | Disrupts natural flora | Allows Candida to thrive |
| Poor Oral Hygiene | Bacteria and plaque accumulation | Promotes infection risk |
| Dentures | Can harbor yeast | Creates a breeding ground |
Symptoms and Indicators
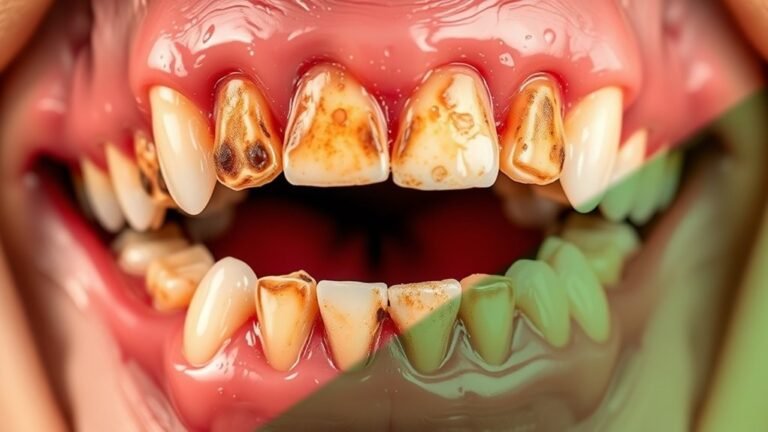
When Candida overgrowth occurs in your mouth, it can lead to a range of noticeable symptoms and indicators of oral thrush. You might experience discomfort or pain, making it difficult to eat or swallow. Here are some common signs to watch for:
- White Patches: These can appear on your tongue, inner cheeks, or gums, resembling cottage cheese.
- Redness and Inflammation: Your mouth may feel sore, and the affected areas could appear red or swollen.
- Bad Breath: An unpleasant odor may develop due to the fungal presence and associated bacterial imbalance.
Recognizing these symptoms early can help you seek appropriate treatment and reduce the risk of further oral infections.
The Connection Between Oral Thrush and Bacterial Infections
Oral thrush, a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida species, can considerably increase your risk of developing bacterial infections. When Candida proliferates, it disrupts the delicate balance of microorganisms in your mouth, allowing harmful bacteria to flourish. This imbalance can lead to conditions such as periodontitis or other oral infections. The inflammation caused by oral thrush can create an environment that’s conducive to bacterial growth, further compromising your oral health. Additionally, the weakened immune response associated with thrush may hinder your body’s ability to fight off these bacterial invaders. Recognizing the link between oral thrush and bacterial infections is vital for maintaining your overall oral hygiene and health, underscoring the importance of timely treatment and professional dental care.
Risk Factors for Developing Oral Thrush
While many factors can contribute to the development of oral thrush, certain conditions and lifestyle choices greatly increase your susceptibility to this fungal infection. Understanding these risk factors can help you take proactive measures to protect your oral health. Here are three key risk factors to take into account:
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or undergoing chemotherapy can weaken your immune defenses, allowing yeast to thrive.
- Antibiotic Use: Taking antibiotics can disrupt the balance of bacteria in your mouth, leading to an overgrowth of Candida fungi.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Neglecting oral care can promote a conducive environment for yeast growth, increasing your risk of infection.
Diagnosing Oral Thrush: What to Expect
Recognizing the signs of oral thrush is the first step toward effective treatment. If you suspect you have oral thrush, a visit to your healthcare provider is essential. They’ll perform an examination and may ask about your symptoms. Here’s what to expect during the diagnosis:
| Step | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Examination | Your provider will inspect your mouth. | Identify white patches |
| Medical History | Discuss your health and medications. | Find underlying causes |
| Culture Test | A sample may be taken for testing. | Confirm the presence of Candida |
| Swab Test | A cotton swab may be used. | Check for fungal infection |
Being prepared for these steps can help streamline your diagnosis and lead to proper care.
Treatment Options for Oral Thrush
When you receive a diagnosis of oral thrush, understanding the available treatment options is essential for effective management. Here are three common treatment approaches to weigh:
- Antifungal Medications: Your doctor may prescribe oral or topical antifungal medications, such as nystatin or fluconazole, to eliminate the Candida overgrowth.
- Home Remedies: You can also try natural remedies like saltwater rinses or baking soda solutions to help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Modifying your diet by reducing sugar intake and improving oral hygiene can support recovery and prevent recurrence.
Preventing Oral Thrush and Maintaining Oral Balance
After addressing the treatment options for oral thrush, it’s important to focus on prevention and maintaining oral balance. Start by practicing good oral hygiene; brush your teeth twice a day and floss daily. Rinse your mouth with water after consuming sugary or acidic foods to reduce yeast growth. Stay hydrated to support saliva production, which naturally combats fungal overgrowth. If you wear dentures, make sure they fit properly and clean them regularly. Limit antibiotic use, as they can disrupt your oral flora. Incorporate probiotics into your diet, such as yogurt or supplements, to help restore balance. Finally, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these can contribute to oral thrush development. Taking these steps can greatly reduce your risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Oral Thrush Be Contagious Between Individuals?
Yes, oral thrush can be contagious. You can spread it through direct contact, sharing utensils, or kissing. It’s crucial to maintain good oral hygiene and avoid close contact if you or someone else has thrush.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Help Prevent Oral Thrush?
To prevent oral thrush, maintain good oral hygiene, limit sugar intake, stay hydrated, manage stress, and avoid smoking. Regular dental check-ups and a balanced diet also support a healthy mouth, reducing your risk.
How Does Diet Affect Oral Thrush Development?
Your diet plays an essential role in oral health; sugary and processed foods can foster yeast growth, while a balanced intake of fruits, vegetables, and probiotics can help maintain a healthy mouth and deter oral thrush.
Are There Alternative Treatments for Oral Thrush?
Yes, you can explore alternative treatments for oral thrush, like coconut oil, probiotics, or apple cider vinegar. Always consult your healthcare provider before trying these options to guarantee they’re safe and effective for your situation.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Untreated Oral Thrush?
Ignoring oral thrush is like neglecting a small leak in your roof; eventually, it can lead to significant damage. Long-term effects can include chronic pain, difficulty swallowing, and an increased risk of systemic infections.
Conclusion
To summarize, oral thrush can act like a warning light on your car’s dashboard, signaling an imbalance that could lead to more serious bacterial infections. Just as ignoring that light can lead to engine trouble, overlooking oral thrush can escalate oral health issues. By recognizing the signs and understanding the risk factors, you can take proactive steps to maintain your oral balance and prevent further complications. Prioritizing oral health is essential for your overall well-being.