How to Detect Early Oral Microbiome Disruption Causing Persistent Infections
To detect early oral microbiome disruption that can lead to persistent infections, watch for signs like chronic bad breath, gum bleeding, and unusual oral pain. Utilize diagnostic tools such as salivary biomarker analysis and 16S rRNA sequencing to assess microbial health. Maintaining good oral hygiene, a balanced diet, and regular dental visits are essential for preventing microbial imbalances. Staying informed about these factors can help you identify issues before they escalate. More insights await.
Key Takeaways
- Monitor for persistent infections, which often signal an imbalance in the oral microbiome requiring further investigation.
- Pay attention to symptoms like chronic bad breath, swollen gums, or oral lesions that may indicate microbial disruption.
- Maintain regular dental visits for professional assessments and early detection of potential oral health issues.
- Utilize diagnostic tools like salivary biomarker analysis to assess the microbial health of your oral cavity.
- Practice diligent oral hygiene and a balanced diet to help prevent shifts in your oral microbiome.
Understanding the Oral Microbiome
Understanding the oral microbiome is essential, as it plays an important role in your overall health. An oral bacterial imbalance can lead to various health issues, making early detection vital. The balance of microorganisms in your mouth influences not only dental health but systemic conditions as well. Utilizing microbial biomarkers can provide insights into the state of your oral microbiome, allowing for timely interventions. Regular assessments of these biomarkers can help identify shifts in microbial composition before they escalate into significant problems. By recognizing the signs of imbalance early, you can implement targeted strategies to restore harmony, ultimately supporting both oral and general health. Prioritizing the health of your oral microbiome is a proactive step toward maintaining overall well-being.
Common Signs of Microbiome Imbalance
You should be aware of several oral symptoms that may indicate a microbiome imbalance. Changes in taste sensation and an increase in cavity formation frequently accompany this disruption. Recognizing these signs early can help you address potential underlying issues effectively.
Oral Symptoms to Watch
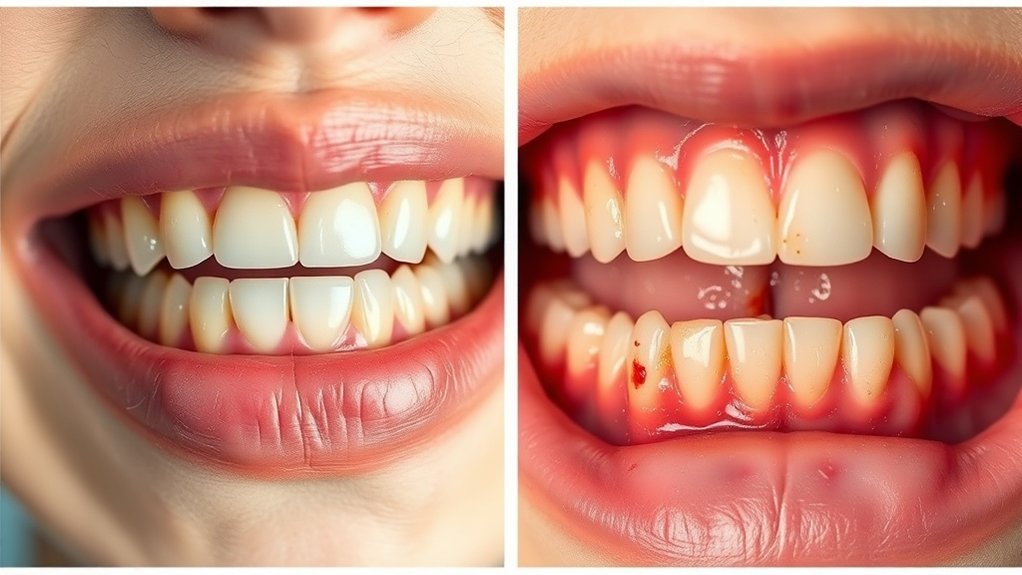
What signs indicate that your oral microbiome might be out of balance? You should watch for persistent infections, such as recurrent gum disease or oral thrush, which often signal underlying oral microbiome disruption. Additionally, if you experience chronic bad breath or unusual plaque buildup, it could indicate a shift in your microbial ecosystem. Increased tooth sensitivity or frequent cavities may also correlate with an imbalanced oral microbiome, adversely affecting your dental health. Changes in the appearance of your gums, such as inflammation or discoloration, further suggest microbial dysbiosis. By recognizing these symptoms early, you can take proactive measures to restore balance and prevent complications associated with persistent infections and other dental issues.
Changes in Taste Sensation
Persistent infections and changes in oral health can often accompany shifts in taste sensation, signaling potential disruptions in the oral microbiome. A disrupted microbiome may lead to altered taste perception due to biofilm formation and changes in microbial diversity. Metagenomic sequencing can identify these shifts, providing insights into the underlying causes.
| Sign of Change | Possible Implication |
|---|---|
| Altered taste perception | Imbalance in microbial community |
| Loss of taste | Disruption in biofilm composition |
| Increased bitterness | Overgrowth of specific bacteria |
| Diminished flavor | Reduced microbial diversity |
Awareness of these changes can prompt earlier intervention, potentially preventing persistent infections and further oral health complications.
Increased Cavity Formation
Increased cavity formation serves as a significant indicator of microbiome imbalance within the oral environment. When the delicate equilibrium of beneficial and harmful bacteria is disrupted, pathogenic species such as Streptococcus mutans proliferate, leading to demineralization of tooth enamel. You might notice increased sensitivity, visible holes, or dark spots on teeth—common signs of this imbalance. Additionally, plaque accumulation can accelerate cavity development, as it harbors these harmful bacteria. Regular dental check-ups and assessments of your oral health are essential for early detection. Maintaining a balanced diet, practicing good oral hygiene, and possibly incorporating probiotics might help restore microbial equilibrium, thereby minimizing cavity formation. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further complications, such as persistent infections or tooth loss.
Factors Contributing to Disruption
Although various factors can influence the stability of the oral microbiome, lifestyle choices and environmental exposures play critical roles in its disruption. Poor oral hygiene practices, such as infrequent brushing and neglecting flossing, can lead to an imbalance in microbial communities. Additionally, tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption create a detrimental environment, fostering pathogenic species. Stress and lack of sleep further exacerbate these issues, as they can impair immune function and alter microbial diversity. Environmental factors, like exposure to pollutants and antimicrobial agents in personal care products, also disrupt microbial homeostasis. By recognizing and addressing these influences, you can take proactive steps to maintain a balanced oral microbiome and mitigate the risk of persistent infections.
The Role of Diet in Oral Health
Your dietary choices greatly influence your oral health, particularly through sugar intake and the consumption of probiotic foods. High sugar levels can lead to harmful bacterial proliferation, disrupting the oral microbiome balance. Conversely, probiotic foods can promote beneficial bacteria, enhancing your overall oral health and potentially mitigating disruption.
Impact of Sugar Intake
As you consume sugar, the oral microbiome undergoes significant changes that can disrupt its delicate balance. High sugar intake fosters an environment conducive to the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, such as Streptococcus mutans. These bacteria metabolize sugars, producing acid as a byproduct, which can lead to enamel demineralization and tooth decay. Additionally, elevated sugar levels can decrease the diversity of beneficial microbes, further tipping the balance toward harmful species. This dysbiosis can initiate a cascade of inflammatory responses, increasing the risk of persistent infections. Monitoring your sugar intake is essential; even seemingly small amounts can have a profound impact on your oral health and microbiome stability. Adopting a balanced diet helps mitigate these risks effectively.
Benefits of Probiotic Foods
Probiotic foods play an essential role in maintaining oral health by promoting a balanced microbiome. These foods help restore beneficial bacteria, counteracting harmful pathogens that can lead to infections. Incorporating probiotics into your diet can enhance saliva production and reduce plaque formation.
| Probiotic Food | Benefits | Recommended Serving |
|---|---|---|
| Yogurt | Supports beneficial bacteria | 1 cup daily |
| Kefir | Enhances immune response | 1 cup daily |
| Sauerkraut | Aids in digestion | ½ cup daily |
| Kimchi | Reduces inflammation | ½ cup daily |
Importance of Oral Hygiene Practices
While many may underestimate the impact of oral hygiene on overall health, maintaining proper practices is essential for preventing disruptions in the oral microbiome. Your daily routine plays a critical role in sustaining microbial balance and avoiding infections. Here are three key practices to incorporate:
Oral hygiene is vital for overall health, supporting microbial balance and preventing infections through daily care practices.
- Regular Brushing: Brush at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and bacteria.
- Flossing: Daily flossing removes food particles and plaque from between teeth, areas where brushes can’t reach.
- Mouthwash Use: Incorporate an antimicrobial mouthwash to further reduce bacterial load and freshen breath.
Recognizing Symptoms of Persistent Infections
How can you identify persistent infections in your oral microbiome? Look for specific symptoms that may indicate microbial imbalance. Persistent bad breath, even after oral hygiene, often signals bacterial overgrowth. You might also notice swollen or bleeding gums, suggesting inflammation and potential infection. Pay attention to any unexplained oral pain or lesions that don’t heal, as these can point to deeper issues. Changes in taste perception or a dry mouth can indicate disruption in microbial equilibrium. Additionally, frequent occurrences of cavities or periodontal disease could signify an underlying persistent infection. Recognizing these symptoms early allows you to take proactive measures, potentially preventing more severe complications related to your oral health.
Diagnostic Tools for Microbiome Assessment
To effectively assess the oral microbiome, various diagnostic tools are available that can provide insights into microbial composition and health. Utilizing these tools can help you identify potential disruptions early on. Here are three key diagnostic methods:
Assessing the oral microbiome with advanced diagnostic tools can reveal crucial insights into microbial health and prevent disruptions.
- 16S rRNA Sequencing: This technique allows for thorough analysis of bacterial diversity by targeting specific genetic markers.
- Metagenomic Sequencing: This provides a broader view by analyzing all genomic material present, offering insights into functional capabilities of the microbiome.
- Salivary Biomarker Analysis: This method evaluates specific biomarkers in saliva that can indicate microbial imbalance or inflammation.
Proactive Steps for Maintaining a Healthy Microbiome
Maintaining a healthy oral microbiome involves several proactive steps that can greatly influence microbial balance and overall oral health. First, practice diligent oral hygiene by brushing twice daily and flossing regularly to remove plaque and food particles. Incorporating antimicrobial mouthwash can further reduce harmful bacteria. Next, focus on a balanced diet rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals while minimizing sugar intake, as sugars can promote pathogenic growth. Staying hydrated is essential; saliva acts as a natural defense mechanism against microbial imbalance. Additionally, consider probiotic supplementation, which can enhance beneficial bacterial populations. Regular dental check-ups guarantee early detection of potential issues, allowing for timely interventions. By implementing these strategies, you can effectively support your oral microbiome’s stability and function.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Stress Impact the Oral Microbiome?
Stress alters your oral microbiome by promoting harmful bacteria overgrowth, reducing beneficial species, and weakening immune responses. These changes can lead to imbalances, increasing susceptibility to infections and impacting overall oral health markedly.
Can Antibiotics Affect My Oral Microbiome Balance?
Imagine a delicate ecosystem thriving in your mouth; antibiotics can disrupt this balance, killing beneficial bacteria alongside harmful ones. This imbalance may lead to issues like overgrowth of pathogens, affecting your oral health greatly.
Are There Genetic Factors Influencing Oral Microbiome Health?
Yes, genetic factors can influence your oral microbiome health. Variations in genes related to immune response and inflammation may affect microbial diversity, potentially impacting susceptibility to conditions like periodontal disease and other oral infections.
How Do Oral Probiotics Help Restore Microbiome Balance?
Imagine your mouth as a thriving ecosystem. Oral probiotics help restore microbiome balance by introducing beneficial bacteria, crowding out harmful species, and enhancing your immune response, ultimately leading to improved oral health and reduced infections.
What Role Does Saliva Play in Oral Microbiome Health?
Saliva acts as a buffer, maintaining pH levels and providing essential nutrients for beneficial bacteria. It also facilitates the removal of harmful pathogens, promoting a balanced oral microbiome and helping prevent infections and diseases in your mouth.
Conclusion
In summary, staying vigilant about your oral microbiome is essential for preventing persistent infections. Research shows that over 70% of individuals with chronic oral infections exhibit signs of microbiome disruption. By recognizing the common signs and understanding the contributing factors, you can take proactive steps, such as improving your diet and maintaining rigorous oral hygiene practices. Monitoring your oral health can help you detect imbalances early, ensuring you preserve a robust microbiome and overall well-being.